What's the difference between LDAP and RADIUS when used for server-based password authentication?
A brief comparison between LDAP and RADIUS.

These days, it's common for security controls to support various types of on-premise authentication methods. A great example would be client VPN authentication on a firewall. Admins can easily point a firewall to an off-device RADIUS or LDAP server. Let's hold up a sec, though. What actually IS the difference between these two particular protocols? What do these methods actually do and how are they different from one another?
Let's find out. :-)
LDAP
LDAP stands for Lightweight Directory Access Protocol. It's a protocol for accessing and modifying information on "directory services".
That term "directory services" is a bit wordy and vague, right? What does that actually mean? Here are some examples:
- User Management - LDAP can maintain user information including names, email addresses, phone numbers, and other relevant details.
- Group Management - LDAP can maintain groups of users (helpful for authentication purposes).
- Resource Management - LDAP can store information about various network resources (e.g. printers, servers, workstations, etc).
These days, a really popular example of LDAP usage is Active Directory Domain Services. It can use LDAP as its underlying protocol to communicate with other directory services.
LDAP as a protocol supports a number of operations that a client can request. This includes things like searching, comparing, maintaining entries, etc. One particular operation of interest is binding. This is an operation that allows the LDAP server to authenticate the user.
RADIUS
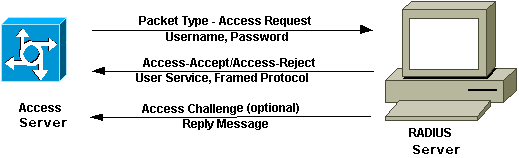
RADIUS stands for Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service. It tends to get lumped in with LDAP as different mechanisms for authentication but they aren't the same. RADIUS is a networking protocol that's specifically designed to provide centralized authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA).
Confused yet? OK, here's some more ways to compare/contrast with LDAP:
- The primary function of LDAP is directory services (storing information about users, groups, and other resources). RADIUS is designed for network access control.
- LDAP uses TCP and often involves multiple requires and responses to retrieve info. That makes it great for complex directory queries. RADIUS on the other hand, uses UDP for faster (albeit theoretically less reliable) communication. The speed makes RADIUS helpful for real-time authentication and authorization decisions.
- LDAP can be secured using TLS/SSL encryption but is not inherently secure by itself. RADIUS uses strong encryption and authentication mechanisms.
Want more info? Check out these resources: