What are the differences between the various IP pool types on FortiGate?
Clarifying some popular terms

Today's topic is a quick one, but it's a question I see coming up from time to time so I thought it would be helpful to write about it. FortiGate IP pools are used for Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) to translate internal private IP addresses to external public IP addresses when traffic leaves the FortiGate. There are different pool types that offer different techniques for this translation/operation.
- Overload (PAT - Port Address Translation) - This is the most common and default IP pool type. It's a many-to-one or many-to-few IP address mapping feature where the FortiGate uses different source port numbers to distinguish between sessions from different internal hosts.
- One-to-one (Static NAT/NAPT) - This creates a direct one-to-one mapping between a specific internal IP address and a specific external IP address. The important thing to note with this mode is that Port Address Translation is disabled (so the source port is preserved).
- Fixed Port Range (Deterministic NAT/CGNAT) - This type of pool is designed for Carrier-Grade NAT (CGNAT) and provides a deterministic mapping between a private IP address and a specific public IP address, along with a fixed block of source port. While it's not strictly a one-to-one for the entire port range, it allows an administrator to predict which public IP and which block of ports a specific internal client will use.
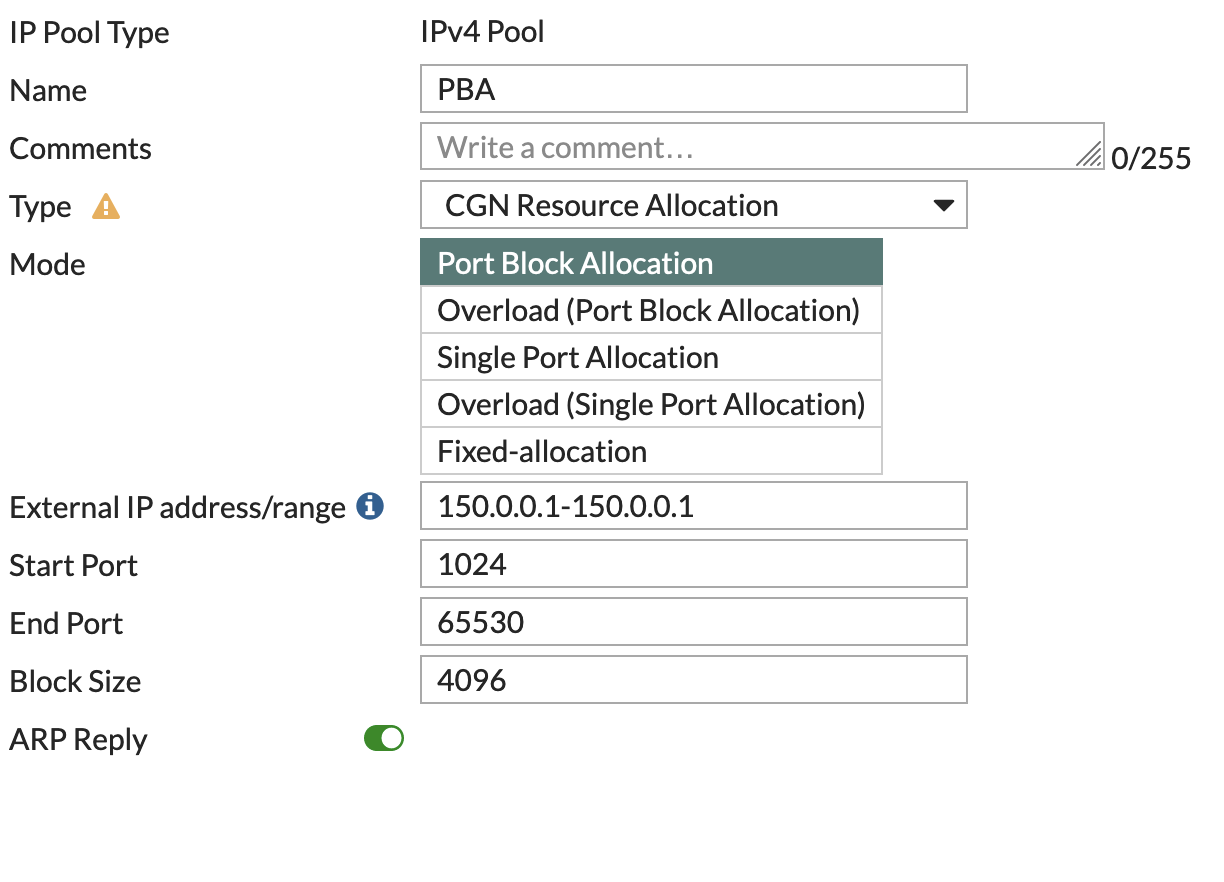
- Port Block Allocation (PBA) - This is similar to the Fixed Port Range but it's more dynamic. When a user initiates a session, a block of ports is assigned from the IP pool. If that block runs out of ports, another block can be assigned. It provides more flexibility than Fixed Port Range for ISPs or large enterprises that need to manage large numbers of users and their outbound connections.
For more information, check out these resources: